Introduction
Keeping machines working is very important. Preventive maintenance helps you fix problems before they happen. This guide shows you how to do it.
What is preventive maintenance?
Maintenance Preventive maintenance means fixing things BEFORE they break. You don’t wait for problems. You check and fix things early.
Think about brushing your teeth. You brush every day. You don’t wait for cavities!
PM includes these simple things:
- Cleaning machines
- Adding oil
- Checking for problems
- Changing old parts
- Looking at machines regularly
The goal is simple. Keep your machines working when you need them.
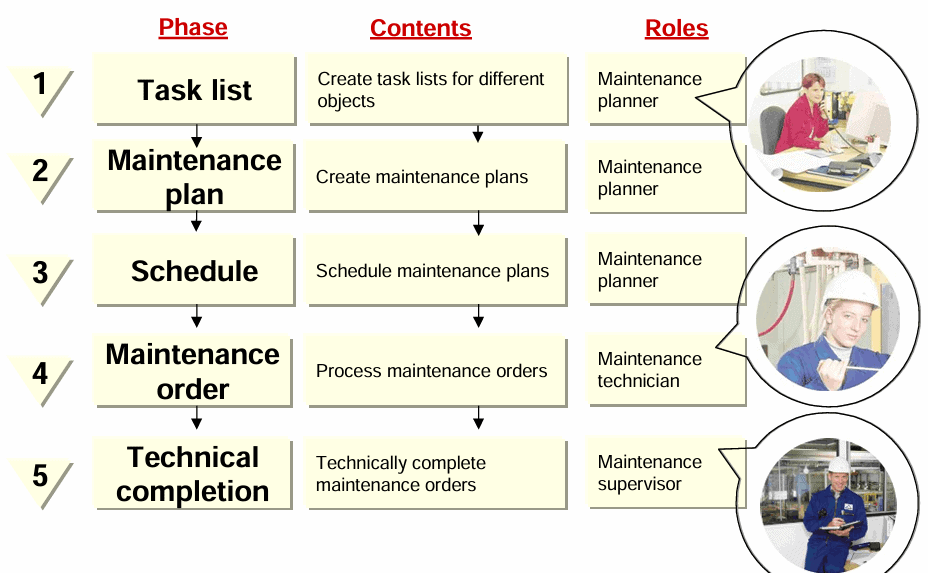
How Maintenance Changed
Long ago, machines were simple. People did most work by hand. Maintenance was not very important.
Today is different. Machines do most work. When a machine stops, work stops. So maintenance is very important now.
Modern maintenance does more than fix broken machines. It keeps machines running well. It helps make good products at a low cost.
Three Types of Maintenance
1. Breakdown Maintenance
You wait until something breaks. Then you fix it.
This is bad because:
- It costs more money
- You can’t plan it
- Work stops suddenly
- It makes big problems
2. Preventive Maintenance (PM)
You fix things before they break. This is smart!
Two ways to do it:
Time-Based:
- Clean every week
- Change oil every month
- Replace parts after set hours
- Like changing car oil every 5,000 miles
Condition-Based:
- Check how machines are doing
- Look and listen for problems
- Use tools to check machine health
- Fix problems early
3. Corrective Maintenance
You fix known problems. You plan when to fix them.
Why PM is Good
PM gives you many benefits:
- Machines work more—less waiting for repairs
- Machines last longer—20% more years
- Save money—10-20% less on repairs
- Safer work—fewer accidents
- Better products—Good machines make quality items
- Easy planning—you know when to do maintenance
- Need fewer spare parts—no big emergency stock needed
Parts of a Good PM Program
1. Know Your Machines
Make a list of all machines. Find the most important ones.
Important machines:
- Stop all work if they break
- Cost a lot to fix
- Make your main products
Start PM with these machines first.
2. Make a Schedule
Decide when to check each machine.
Scheduled by:
- Time (weekly, monthly)
- Hours used (every 1,000 hours)
- What checks show you
- Machine readings
3. Make Work Lists
For each job, write down:
- What to do
- What tools needed
- What parts needed
- How long it takes
- Who does it
4. Choose Your Way
Pick the best method for each machine:
Time-Based—Do work at set times. Easy and simple.
Use-Based – Do work after the machine runs a certain time. Good for busy machines.
Condition-Based—Do work when checks show you need to. Saves money but needs more skill.
Smart Maintenance
Smart maintenance is even better. You use special tools. These tools tell you exactly when machines need work.
Ways to check:
- Check vibration
- Check heat
- Test oil
- Use sound tests
- Check electricity
Good things about this:
- Stop machines before big damage
- Plan the best time
- Only fix what needs it
- Safer work
- More production
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)
TPM is special. Workers fix their own machines. This makes them care more.
What “Total” Means:
- Total Effect—Make best profit
- Total PM—Plan for machine’s whole life
- Total People—Everyone helps
Main TPM Work:
- Fix problem areas
- Workers maintain machines
- The team does planned work
- Train everyone
- Buy easy-to-fix machines
- Focus on quality
- Keep records
- Safety first
How to Measure Success
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE)
This shows how well maintenance works.
OEE = How Much × How Fast × How Good
What this means:
- How Much Time the Machine Works
- How Fast—Speed compared to design
- How Good—Number of good products
Good targets:
- How Much: over 90%
- How Fast: over 95%
- How Good: over 99%
Other Things to Track:
- How often machines break
- How long fixes take
- Cost per product
- Emergency repairs
- Bad products made
Steps to Start PM
Step 1: Check Now
Look at all the machines. Write down:
- Their condition
- What you do now
- What problems happen
Step 2: Fix Current Issues
Fix broken machines first. Make everything work right.
Step 3: Keep Records
Write down all work. Use:
- Notebook
- Computer file
- Software
Track every job.
Step 4: Make Schedule
Plan when to check each machine. Start simple. Make it better later.
Step 5: Add Checks
Start checking machines often. This shows when work is needed.
Step 6: Get Better
Look at results every few months. What works? What doesn’t? Improve it.
Workers Help with Maintenance
Teaching workers to help is very important.
Workers can:
- Clean daily
- Add oil
- Check for loose parts
- Listen for odd sounds
- Report problems
Seven Steps:
- Clean machine fully
- Stop dirt problems
- Make simple rules
- Learn to check
- Check work area
- Do regular work alone
- Run own machine
Why this helps:
- Workers care more
- Less damage
- The team focuses on hard jobs
- Find problems early
Common Problems
Problem 1: People Resist Change
Fix: Explain benefits. Show savings. Train well.
Problem 2: Not Enough Resources
Fix: Start small. Pick 5 key machines. Grow later.
Problem 3: No Records
Fix: Start today. Use a notebook. Build over time.
Problem 4: Can’t Stop Production
Fix: Work with managers. Do PM during slow times.
Real Costs
Some think maintenance just costs money. Wrong! Good maintenance SAVES money.
Remember this: Skipped maintenance costs MORE later!
Hidden costs of bad maintenance:
- Lost work time
- Lost customers
- Wasted power
- Bad products
- New machines sooner
- Worker injuries
- Environmental harm
Money saved with PM:
- 20% less downtime
- 20% longer life
- 10-20% less repairs
- 10-20% lower total cost
Using Computers
Computer systems help maintenance. They are called MMS or CMMS.
What they do:
- Track machines
- Schedule work
- Manage parts
- Save history
- Show reports
- Make work orders
- Track costs
New technology:
- Sensors watch 24/7
- Alerts for problems
- Predicts failures
- Collects data
This makes work smarter and easier.
Final Thoughts
Every business needs PM. It’s not optional now.
Keys to win:
- Start simple
- Include everyone
- Keep records
- Measure results
- Always improve
Find your balance. Mix preventive work with fixing breaks. It depends on:
- Machine age
- Machine importance
- What you make
- Your budget
Remember: PM is not a cost. It’s an investment. It helps you:
- Make more
- Better quality
- More money
- Safer work
Start PM today. Your machines will thank you!
The best time to start was yesterday. The next best time is now.
